Variable selection for causal inference
What If: Chapter 18
Elena Dudukina
2022-03-23
1 / 11
18.1 The different goals of variable selection
- No adjustment needed when the aim is prediction
- Include any variables that improve predictive ability
- Automated variable selection for prediction models
- Lasso and other regression algorithms
- Non-regression algorithms, e.g. neural networks
- Use cross-validation to fine tune predictive accuracy
- Adjustment for confounding and other biases when the aim is causal answer
- Automated approaches for variable selection are arguably less appropriate due to the risk of introducing bias
- Subject matter knowledge
2 / 11
18.2 Variables that induce or amplify bias
- Unbiased causal effect estimation needs no adjustment
- Adjusting for L creates selection bias under the null
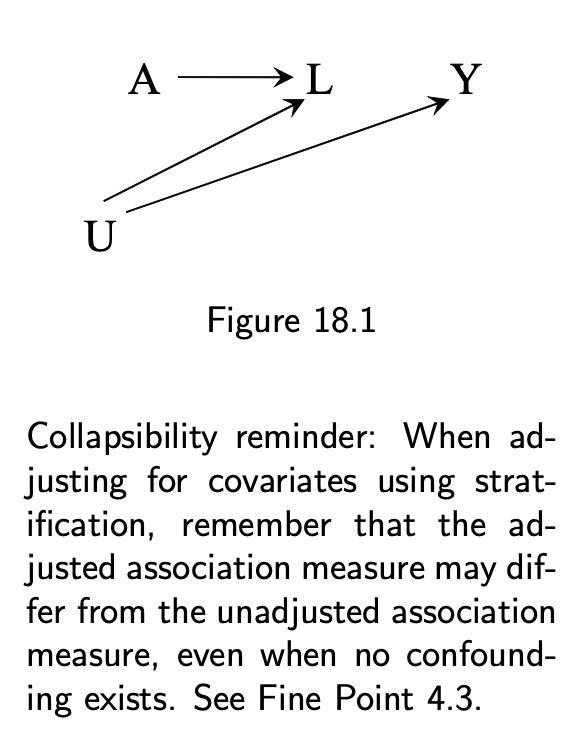
3 / 11
18.2 Variables that induce or amplify bias
- Selection bias under an alternative
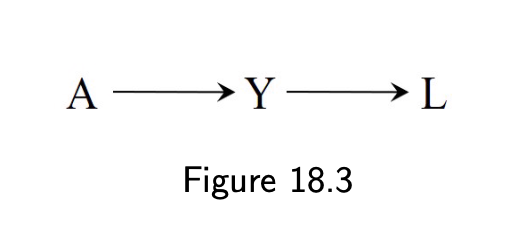
4 / 11
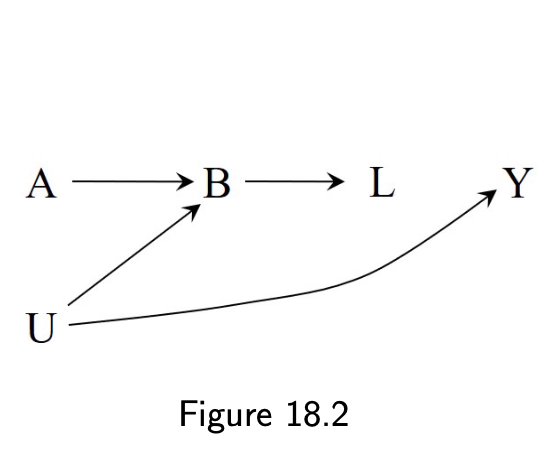
18.2 Variables that induce or amplify bias
- Overadjustment for a mediator (18.4)
- Adjust for post-treatment L (18.5)
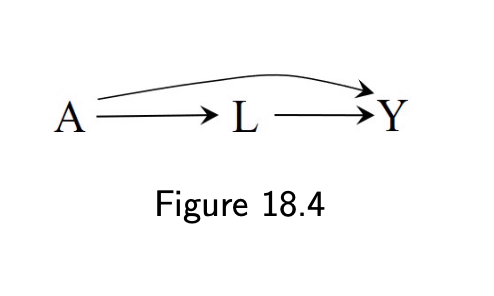
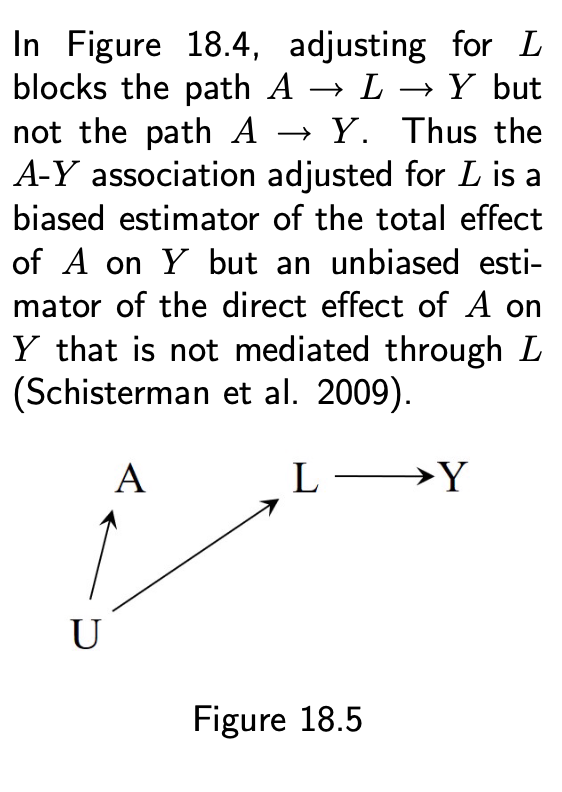
5 / 11
18.2 Variables that induce or amplify bias
- M-bias
- L is not a confounder
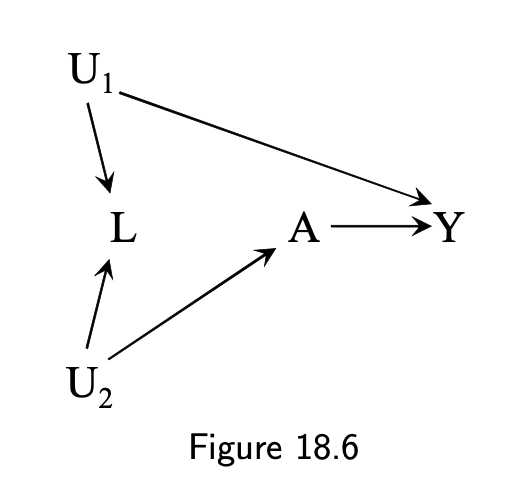
6 / 11
18.2 Variables that induce or amplify bias
- Bias amplification when adjusting for instrument Z
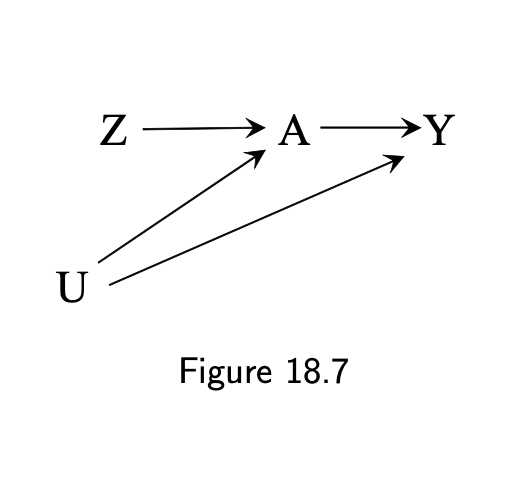
7 / 11
18.3 Causal inference and machine learning
- ML algorithms do not guarantee that the selected variables eliminate confounding
- Doubly robust estimator gives smaller bias and smaller, however the variance of the estimate may be wrong
- Wrong coverage: fail to trap the causal parameter of interest at least 95% of the time
- ML algorithms are statistical black boxes with largely unknown statistical properties
8 / 11
18.4 Doubly robust machine learning estimators
- Split the sample
- Apply the predictive algorithms to the training sample in order to obtain estimators
- Compute the doubly robust estimator of the average causal effect in the estimation sample using the estimators from the training samples
9 / 11
18.5 Variable selection is a difficult problem
Doubly robust machine learning does not solve all problems
Available subject-matter knowledge are insufficient to identify all important confounders or to rule out variables that induce or amplify bias
No algorithm is optimal in all settings
Implementation
No guarantee that estimate's variance will be small enough for meaningful causal inference
Tension between including all potential confounders to eliminate bias and excluding some variables to reduce the variance is hard to resolve
- Developing a clear set of general guidelines for vari- able selection may not be possible
10 / 11
References
- Hernán MA, Robins JM (2020). Causal Inference: What If. Boca Raton: Chapman & Hall/CRC (v. 30mar21)
- A Crash Course in Good and Bad Controls paper
- A Crash Course in Good and Bad Controls blog
- Good & Bad Controls Statistical Rethinking 2022 Lecture 06
- Econometrics: Control Variables video by Nick Huntington-Klein
- Targeted Learning in R: Causal Data Science with the tlverse Software Ecosystem
11 / 11